News
Blog Safebear - CTA towards Safebear solution - Employer brand (inclusivity, values) - French startup brand inno, AI - Protection prevention parental control
News, tips and best practices by SafeBear!

What Does the European Directive on Fighting Cyberbullying Say?
The Digital Services Act brings many changes for protecting internet users on social media. Here's what you need to know!
Nicolas

Nicolas
What Does the European Directive on Fighting Cyberbullying Say?
The Digital Services Act brings many changes for protecting internet users on so

Romain
I Am a Witness to Cyberbullying, What Should I Do?
If you witness cyber violence, here's how to help the victim without standing id

My Child is a Bully, What Should I Do?
Harassment - Is your child the perpetrator? React firmly, with pedagogy thanks t
Romain

The New Digital Space Regulation Law: SREN
Cyber protection - In brief, here's what you need to know about the SREN bill, a
Safebear

How to Detect if a Child is Being Cyberbullied?
Cyberbullying - Your child isn't telling you anything but something seems off in
Romain

PHAROS: The Virtual Guardian of Online Legality
Cyber protection - What is Pharos, the platform for reporting illegal online con
Safebear
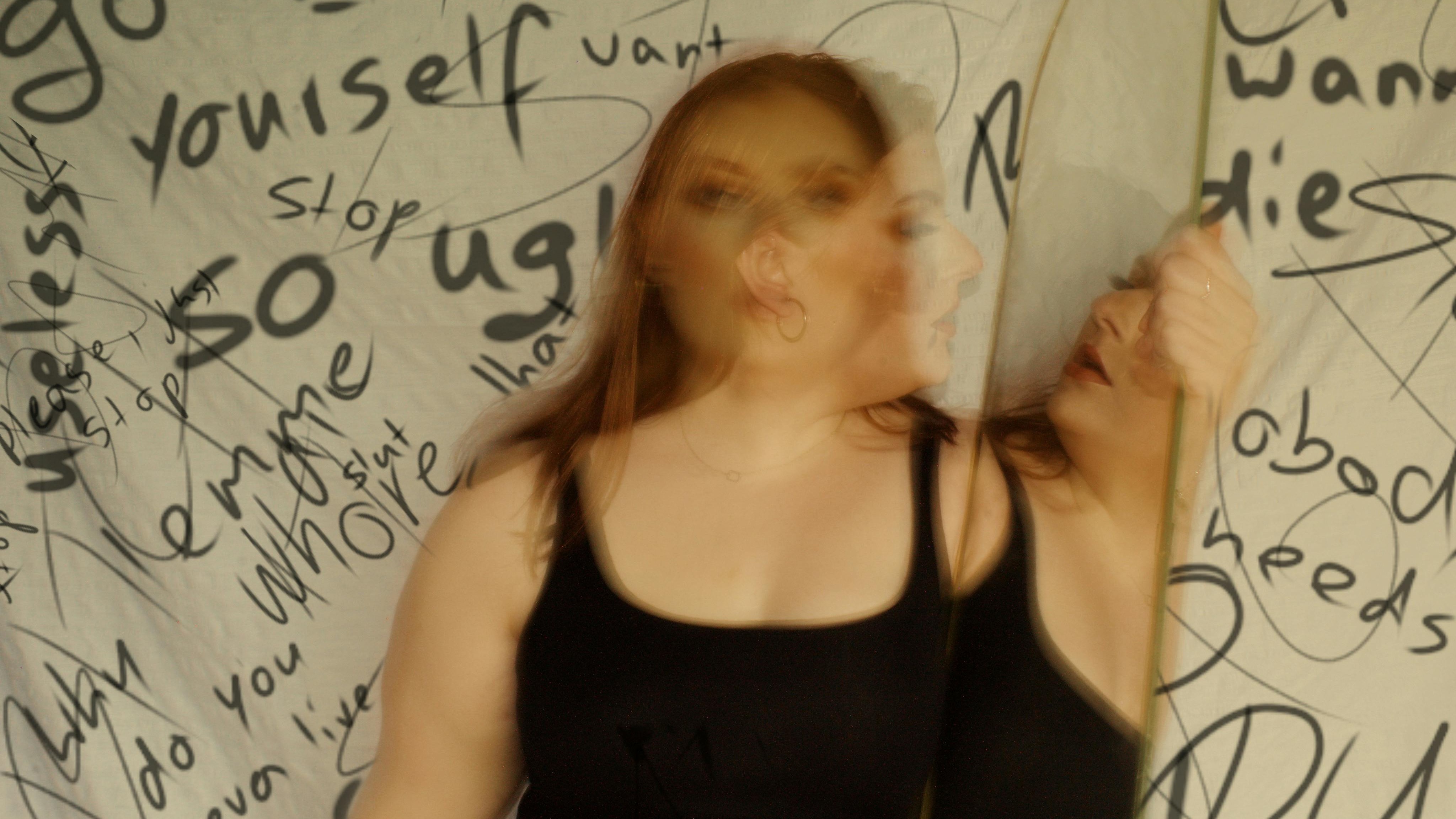
Cyberbullying: Definition and Regulations
Cyberbullying - Here's everything you need to know about this modern-day offense
Nicolas

How to Talk About Cyberbullying with Your Child?
You won't always know what's happening on your children's smartphones, here are
Romain

How to React to Social Media Harassment?
Cyberbullying - Regardless of your age, gender, beliefs or origins, here are som
Antonina
Mon Mar 18 2024 00:00:00 GM
French innovation that secures online exchanges for everyone
The Safebear App
Practical Information